Cell Division Biology Diagrams The assembly and dynamics of the mitotic spindle rely on the shifting balance between opposing plus-end-directed and minus-end-directed motor proteins. Three classes of spindle microtubules can be distinguished in mitotic animal cells they play an active part in spindle formation. The influence of the chromosomes can be demonstrated by
A computational model for the formation of lamin-B mitotic spindle envelope and matrix. Interface Focus 4 , 20130063 (2014). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar The mitotic spindle in yeast (A, left) is formed from spindle pole bodies (A, right) that are composed of five subcomplexes (B). (A, left) Immunofluoresence of a large-budded mitotic yeast cell showing SPBs marked by Spc42-GFP (green), microtubules (red), and DNA (blue) and electron micrograph (A, right) showing trilaminar ultrastructure.

Spindle apparatus Biology Diagrams
In all eukaryotes, morphogenesis of the microtubule cytoskeleton into a bipolar spindle is required for the faithful transmission of the genome to the two daughter cells during division. This process is facilitated by the intrinsic polarity and dynamic properties of microtubules and involves many proteins that modulate microtubule organization and stability. Recent work has begun to uncover Mitotic spindle formation begins as cells transition from interphase into mitosis. As the nuclear envelope breaks down in prophase, microtubules emanating from centrosomes undergo rapid polymerization and depolymerization, probing the intracellular space for chromosomes. This dynamic behavior, driven by tubulin instability, enables efficient
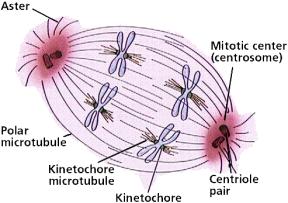
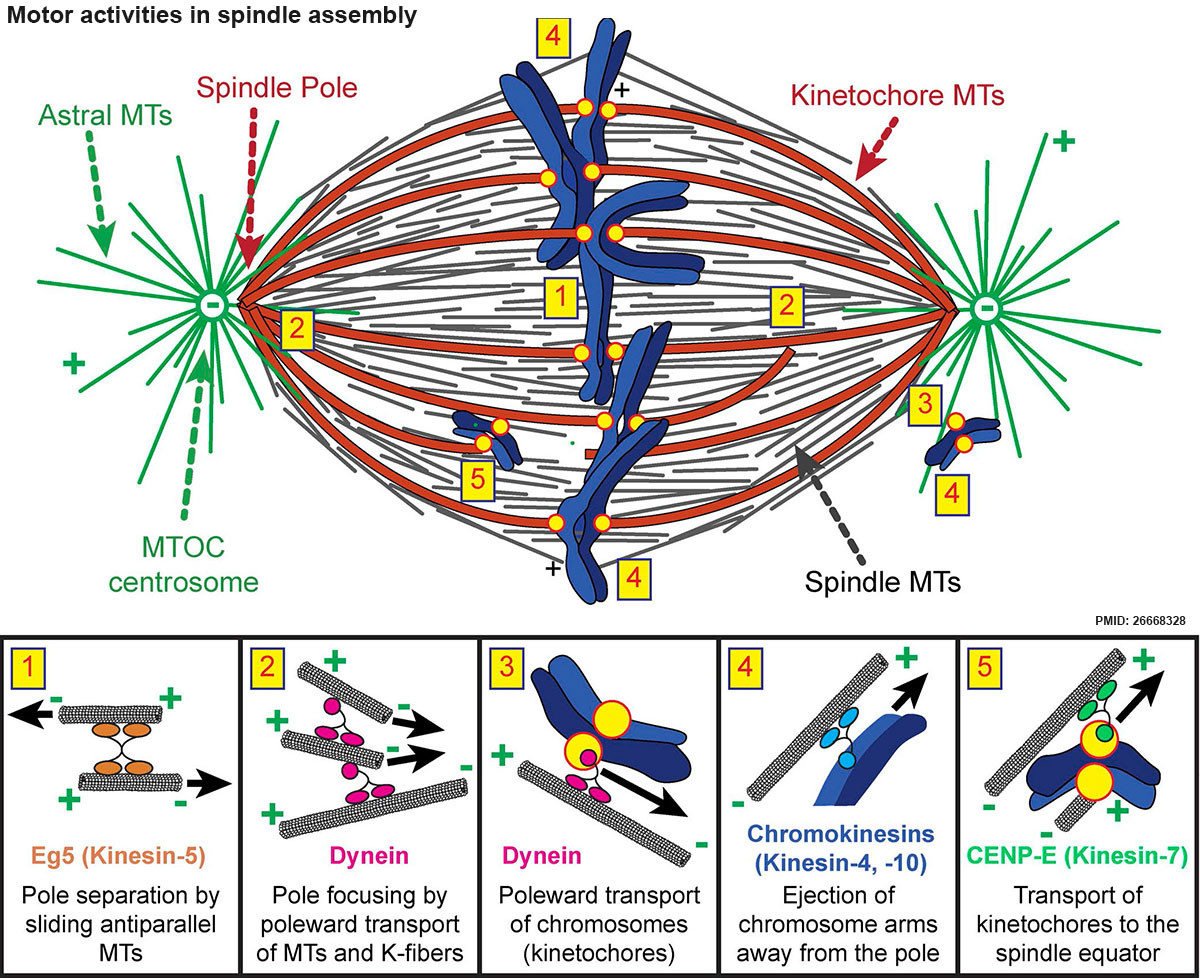
The activity of spindle MAPs is essential for spindle formation and can be grouped into several activity classes . First, MT nucleation factors generate MTs from spatially discrete sites, termed MT organizing centers (MTOCs), that play a key role in constructing the mitotic spindle. (A) Features of the metaphase mitotic spindle. With their minus ends tethered at the spindle poles, microtubules extend either to the kinetochores of paired chromatids (kinetochore fibers), to the central spindle where they form an overlapping antiparallel array (interpolar microtubules), or away from the spindle towards the cell cortex (astral microtubules). Mitotic spindle formation is a critical event that takes place during prophase. Several events of mitosis depend on the mitotic spindle, which forms in the cytoplasm during prophase.

